Download PDF
Client Requirement
Client required an online survey system for restaurants. It should be a cross platform mobile application that allows users to look for restaurants, fill their survey forms and win vouchers or coupons via Android, iPhone or Blackberry. The app makes use of location based technology.
Client’s specific requirements for the application were:
- Mobile application that is location based and sends alerts to users about nearby restaurants
with the best deals. - Survey form for the restaurant loads on the user’s mobile.
- The app must allow rewards setting for customers.
- The UI must be flexible to enable restaurant owners to build custom and interactive surveys.
- Social media integration for users to instantly share.
- Facility to block users for the purpose of fake survey reduction.
- Advanced filtering and sorting techniques.
- Facility for data archival.
- Quick data assimilation as per the current trends, demographics and fashion.
- Graphical reports with detailed analysis and the ability to print it.
Challenges
The team faced the following challenges:
- Fetching of restaurant data within a specified range required setting up of client and server
interaction. - Showing users the restaurants that are located within a specified range.
- Synchronization of surveys, reports and images as per user’s accounts on devices.
Technologies Used
| Xcode 4.2.1 | Xcode is a tool, also called as IDE, used to develop iOS and Mac applications. It is a main component of Xcode toolset. It groups most of the tools needed to develop software in a streamlined and interactive manner. |
| Core Data Framework | The Core Data framework provides generalized and automated solutions to common tasks associated with object life-cycle and object graph management, including persistence. |
| iOS sdk 5.0 | iOS is a software development kit used to develop iPhone, iPad applications specific to OS versions as required by the user. |
| MVC | The model–view–controller framework separates the representation of information in a computer program from the user’s interaction with it. The model consists of application data and business rules, and the controller mediates input, converting it to commands for the model or view. |
Manpower
| Project Leader | 1 |
| Developers | 1 |
| Designers | 1 |
| Quality Assurance Testers | 1 |
Planning
The following development approach was used taking into account the numerous functionalities that the site needed to incorporate:
- In order to manage backup data volume, high level coding standards were followed. Synchronization of data with server was also required for recent data modulations.
- The application had to be designed to be interactive and user friendly.
- Synchronization of new data for backup with our database required attention and planning to
generate desired results. - The User interface layer designed as per iPhone standards.
Architecture
Application Lifecycle
The application lifecycle consists of a sequence of events that occur when you launch the application and until you close or terminate it. On the iPhone or iPAD, a user taps on the application icon on the home screen to launch it. During this process, the application shows some transitional graphics before actual launch and the calling of the main function. The UIKit then handles the bulk of the initialization work. And finally loads the user interface. While this loop is executing, the UIKit coordinates the delivery of events to custom objects and responds to commands issued to it by the application. Whenever the application received a quit command from user, the UIKit notifies the app and the termination process begins.
The life cycle of an iPhone application is shown below:
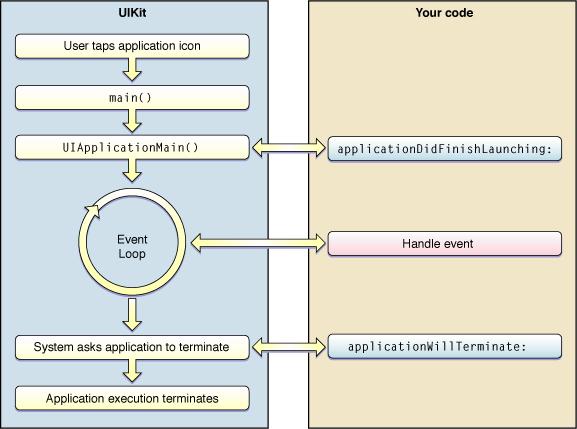
At initialization and termination, UIKit sends specific messages to the application’s delegate object to let it know what is happening. During the event loop, UIKit dispatches events to your application’s custom event handlers.
Event Handling Cycle
After the UI Application main function initializes the application, the infrastructure needed to manage the events and drawing cycle are started. With user interaction with the device, iPhone/iPad OS detects all the touch events and places them in a queue. The event handling infrastructure is responsible to deliver it to the object that is best suited to handle it. In the iPhone Multi-Touch event model touch data is included in a single event object. To track individual touches, the event object contains touch objects. As the user places fingers on the screen, moves them around and finally removes them from the screen, the system reports the changes for each finger in the corresponding touch object.
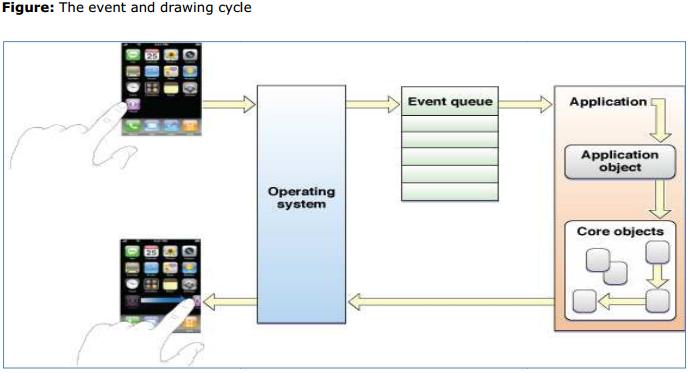
When an application is launched, the system creates a process and a single thread for the app. This becomes the main thread and the UI application object sets up the main run loop and the application’s event handling code is configured. The events are queued until they can be processed by the application’s main run loop.
The MVC Architecture (Model-View-Controller)
Model: is an object that knows all the data that needs to be displayed. Model is aware of all the operations that can be applied to transform an object. It represents the data of an app. Model is what defines the enterprise data and the business rules applied to govern the access to and updates of the data. The Model does not hold any information about the presentation of data to the browser or how the browser will display it.
View: This is what will take care of the presentation of the data for the application. The view object refers to model for information. It uses queries to get information and then renders it. It does not depend on the app logic. In fact, there are no changes to the view even if the business logic changes. View maintains consistency in its presentation even if there are changes in the model.
Controller: Users send commands to the application always via the controller. The controller intercepts the command and requests view and model to take appropriate action. After appropriate action is taken, the controller also forwards the correct view to the user. The views and controllers work closely together to generate the desired results.



